Master AI & Build your First Coding Portfolio with SkillReactor | Sign Up Now
Understanding the Structure of JWT
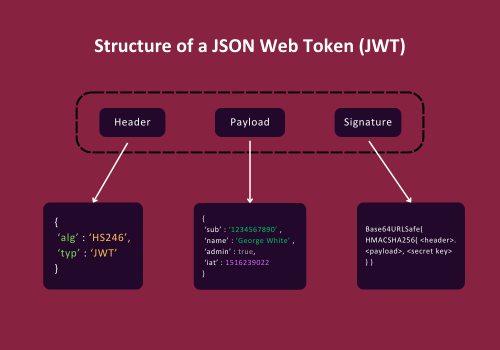
A JSON Web Token (JWT) is a sophisticated yet elegant means of representing claims securely between two parties. Its structure is ingeniously segmented into three distinct parts: the Header, the Payload, and the Signature. Each of these components plays a crucial role in the token's functionality and security.
- Header: The header typically consists of two key parts: the type of the token, which is JWT, and the signing algorithm being used, like HMAC SHA256 or RSA. It's formatted as a JSON object and then Base64Url encoded. The header essentially informs the receiving party about how to process the token.
{ "alg": "HS256", "typ": "JWT" }
- Payload: The payload contains the claims. Claims are statements about an entity (usually the user) and additional data. The payload can include information like the user ID, role, and token expiration time. Like the header, the payload is also Base64Url encoded. There are three types of claims: registered, public, and private.
{ "sub": "1234567890", "name": "John Doe", "admin": true }
- Signature: The signature is created by taking the encoded header, encoded payload, a secret, and the algorithm specified in the header, and then signing it. This process ensures that the token has not been altered during transit. The signature is what makes the JWT secure and trustworthy.
HMACSHA256( base64UrlEncode(header) + "." + base64UrlEncode(payload), secret)
The creation of a JWT involves encoding the header and payload and then signing these together. The cryptographic signing validates the authenticity and integrity of the token. If any part of the header or payload is altered, the verification process will fail, thus ensuring the token's security.
Code snippet: A simple JWT token example with a breakdown of its components:
Header: eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9 Payload: eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6IkpvaG4gRG9lIiwiYWRtaW4iOnRydWV9 Signature: TJVA95OrM7E2cBab30RMHrHDcEfxjoYZgeFONFh7HgQ